States
States can correspond to stages of a particular process. For example, orders can be new, confirmed, in progress, completed, or canceled. On the other hand, states can characterize something in general: products can be in stock or sold out, while customers can be new, loyal, problematic, or lost.
The states a record can be in are determined by its dataset. Depending on the record’s state, users’ access to it and its property’ data may vary. For example, while an order is being delivered, the courier has access to the customer’s phone number—but not after delivery. Or: available products are accessible to the manager, while sold-out ones are not.
Since states belong to datasets, managing them requires going to the settings of the relevant dataset. To do this, activate configuration mode by clicking the corresponding toggle at the bottom of the sidebar, then select “Configure” from the context menu next to the dataset name in the sidebar catalog or next to its name in the main area. On the dataset configuration screen, states are displayed horizontally at the top.
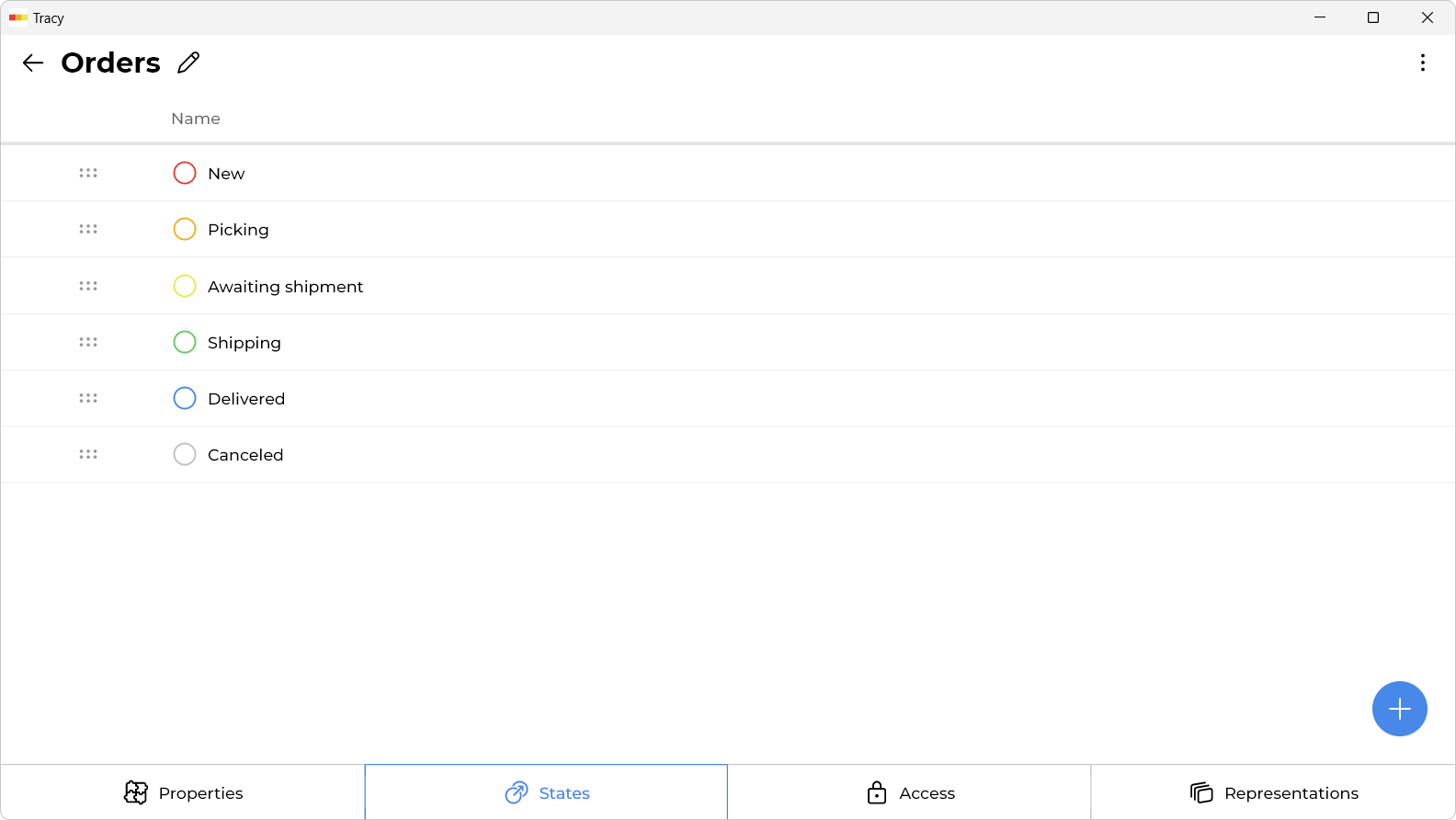
Please note: if the configuration mode toggle is not available, it means you do not have access to system settings. In this case, contact your workspace administrator or owner.
Adding a State
To add a state, click the “+” icon to the right of the last one.
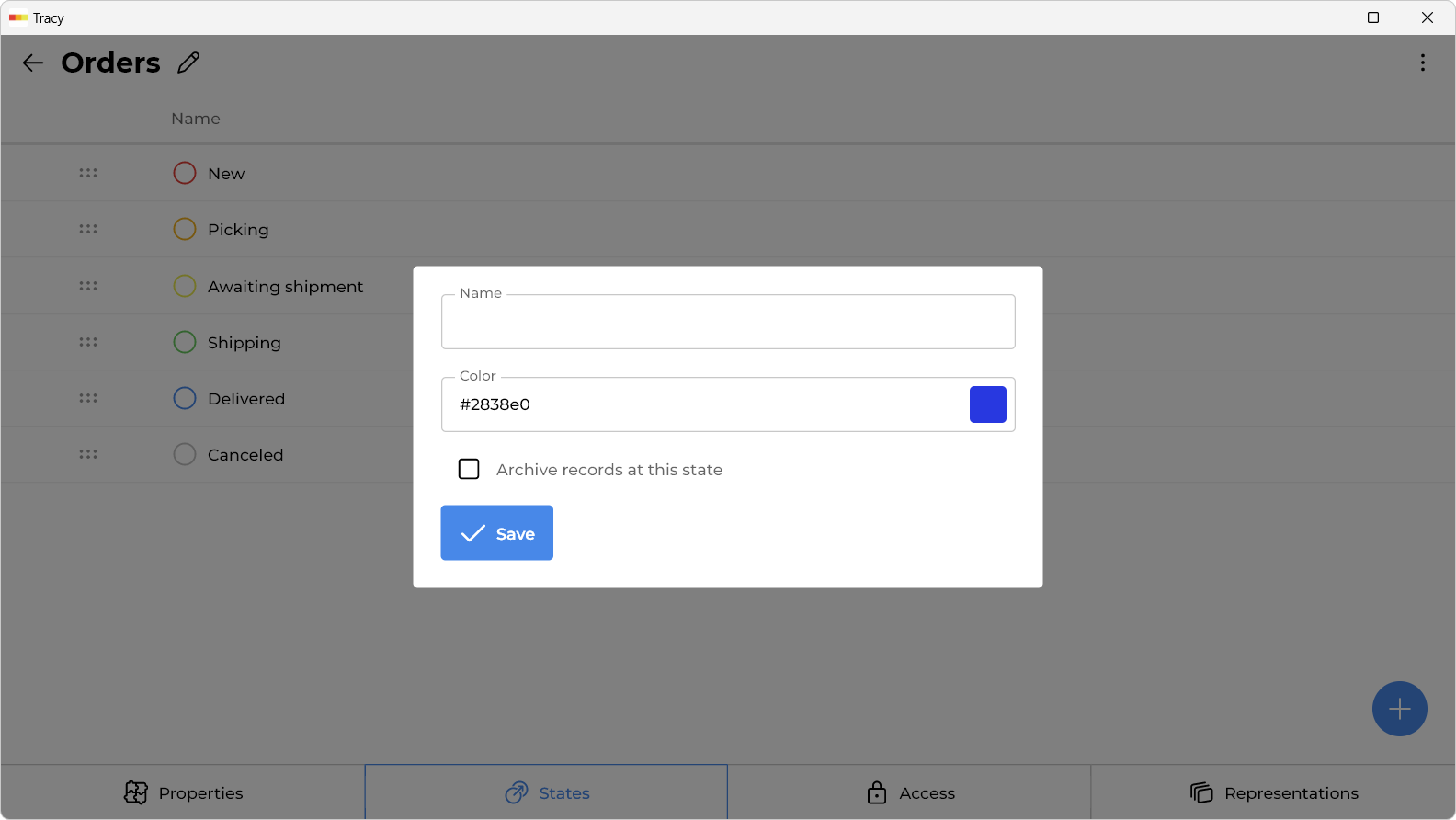
In the window that opens, specify the name of the state and its color, then click “Save” button.
Renaming or Recoloring a State
To change the name or color, click on the state or select “Edit” from its context menu, make the necessary changes in the window that opens, and click “Save”.
Reordering States
To change the order of states, drag a state to the desired position using the nine-dot handle to the left of its name.
Deleting a State
To delete a state, click on it and select “Delete” from the drop-down context menu in the window that opens.
Please note: a state cannot be deleted if there is at least one record in it (including the archive and trash).